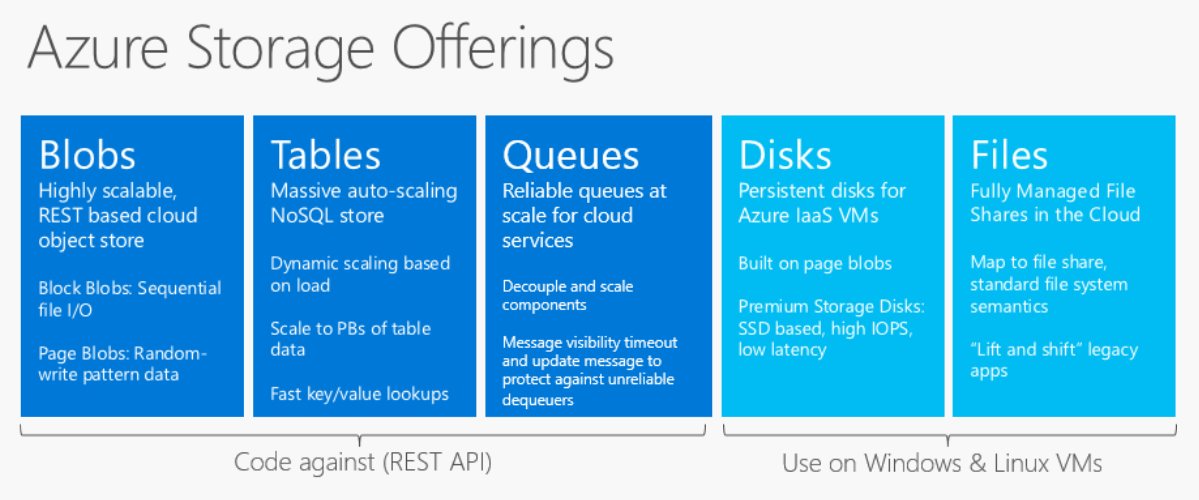
The data in your Microsoft Azure storage account is always replicated to ensure durability and high availability. Azure offers the following storage types
When you create a storage account, you can select one of the following replication options:
- Locally redundant storage (LRS)
- Zone-redundant storage (ZRS)
- Geo-redundant storage (GRS)
- Read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS)
Locally redundant storage (LRS)
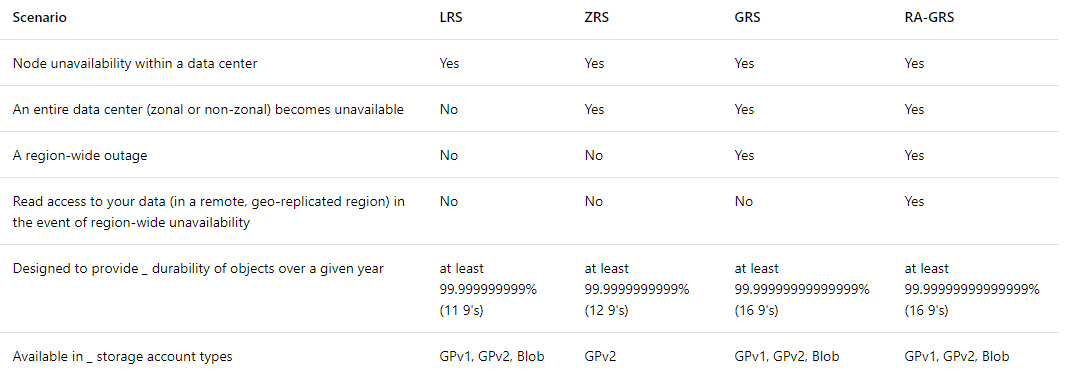
Locally redundant storage (LRS) is designed to provide at least 99.999999999% (11 9’s) durability of objects over a given year by replicating your data within a storage scale unit. LRS is the lowest cost replication option and offers the least durability compared to other options. If a datacenter-level disaster (for example, fire or flooding) occurs, all replicas may be lost or unrecoverable.
Zone-redundant storage (ZRS)
Zone Redundant Storage (ZRS) synchronously replicates your data across three storage clusters in a single region. Each storage cluster is physically separated from the others and resides in its own availability zone (AZ). Each availability zone, and the ZRS cluster within it, is autonomous, with separate utilities and networking capabilities. Your data will remain resilient if a zone becomes unavailable.
ZRS is generally available in the following regions:
- US East 2
- US Central
- North Europe
- West Europe
- France Central
- Southeast Asia
Geo-redundant storage (GRS)
Geo-redundant storage (GRS) is designed to provide at least 99.99999999999999% (16 9’s) durability of objects over a given year by replicating your data to a secondary region that is hundreds of miles away from the primary region. If your storage account has GRS enabled, then your data is durable even in the case of a complete regional outage or a disaster in which the primary region is not recoverable.
Read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS)
Read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS) maximizes availability for your storage account. RA-GRS provides read-only access to the data in the secondary location, in addition to geo-replication across two regions.
When you enable read-only access to your data in the secondary region, your data is available on a secondary endpoint as well as on the primary endpoint for your storage account. The secondary endpoint is similar to the primary endpoint, but appends the suffix –secondary to the account name. For example, if your primary endpoint for the Blob service is myaccount.blob.core.windows.net, then your secondary endpoint is myaccount-secondary.blob.core.windows.net. The access keys for your storage account are the same for both the primary and secondary endpoints.
The following table summarizes those options: